7 Treatments for Presbyopia Correction
-

Presbyopia is an unavoidable age-related condition that causes near vision problems in people aged 40 and over. The gradual loss of vision can interfere with simple everyday tasks like reading, operating a smartphone or tablet, or working on a computer. The good news is that presbyopia can be easily diagnosed through a routine eye exam, and there are a number of treatment options available to help restore near vision.
Check out these seven common treatments for presbyopia correction:
-
1. Eyeglasses
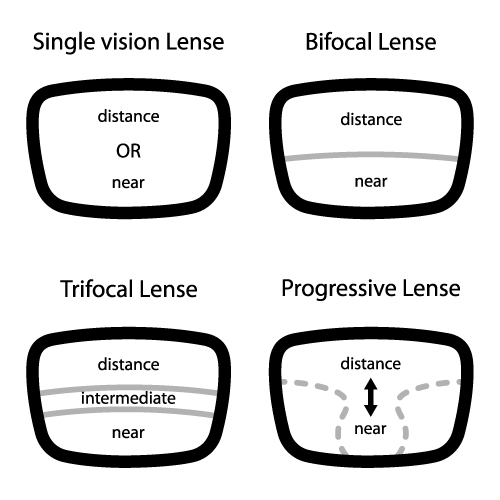
By far the most common (and simplest) treatment for presbyopia is bifocal or progressive lens eyeglasses.
A bifocal lens is split into two sections. The larger, primary section corrects for distance vision, while the smaller, secondary section allows you to see up close.
Progressive lenses function in a similar manner, except that the sections of the lens optimized for distance and near vision are more blended (as opposed to the two distinct zones that characterize bifocals).
Although a simple and cheap option for correction, there can be associated hassles and aesthetic concerns with eyeglasses, which is why some people opt for an alternative solution such as contact lenses or surgery.
-
2. Contact Lenses

Multifocal and monovision contact lenses are very common treatments for presbyopia.
Multifocal contact lenses function in a manner similar to bifocal eyeglasses and are designed to provide clear vision across various focal points. Patients can work with their eye doctor to find the best fit, whether a soft lens, a rigid gas permeable lens, or a hybrid. They also have the added bonus of being available as disposable lenses.
Monovision contact lenses offer different prescriptions for each eye; one for distance vision and one for near vision. This can be problematic for some people who have a difficult time making the adjustment. Visual acuity and depth perception can be affected.
Both eyeglasses and contact lenses are temporary solutions for presbyopia that require ongoing maintenance. These days more people are opting for a permanent treatment through corrective surgery.
-
3. Monovision LASIK

Although LASIK cannot treat the root cause of presbyopia, there are LASIK variations that can help reduce your need for reading glasses or bifocals.
Monovision LASIK is a procedure that corrects the dominant eye for distance vision while leaving the less-dominant eye nearsighted. Why? Because a mildly nearsighted eye is able to see things up close without reading glasses. The only problem is that distance vision with monovision LASIK is often not as crisp as it would be without the nearsightedness. Many people find this to be an acceptable tradeoff for improved near vision and, as such, Monovision LASIK is the most widely used surgical correction for presbyopia.
-
4. Multifocal LASIK

Whereas monovision LASIK improves distance vision in one eye and near vision in the other, multifocal LASIK (also called PresbyLASIK) creates multiple “power zones” across the surface of the cornea to improve the depth of clear vision focus at any distance.
Multifocal LASIK is not yet approved by the FDA, though it is progressing through the clinical trial process and has been approved in several other countries.
-
5. Corneal Inlays
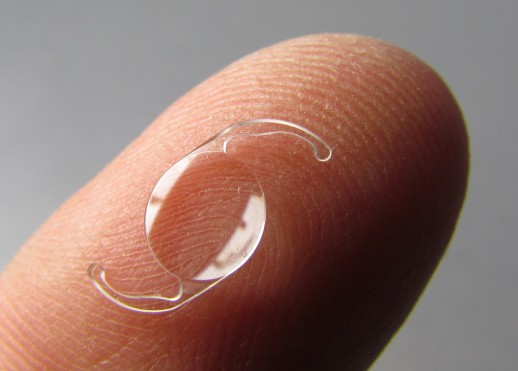
Corneal inlays are tiny implantable lenses that are surgically placed in the cornea to improve vision affected by presbyopia. There are currently two FDA-approved corneal inlays available, each of which works in a slightly different fashion.
The KAMRA corneal inlay is implanted in the non-dominant eye where its pinhole design allows it to extend the patient’s range of vision from near to far.
-
6. Conductive Keratoplasty
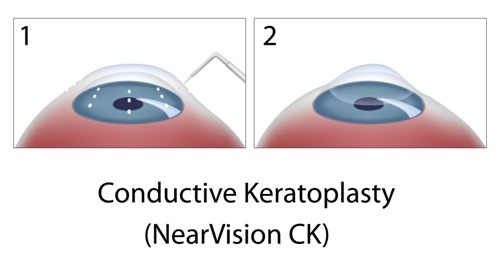
Also called NearVision CK, conductive keratoplasty incorporates the use of a handheld probe that sends radio waves to targeted spots on the cornea to adjust its shape. It is most often performed on only one eye, making it a form of monovision correction.
In addition to being used as a treatment for presbyopia, conductive keratoplasty has been studied as a treatment for other eye conditions including keratoconus and astigmatism.
-
7. Refractive Lens Exchange
Refractive lens exchange (RLE) is an invasive procedure that involves replacing the natural lens of the eye with an artificial alternative. RLE treatment for presbyopia is similar to that used for cataract surgery. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) replacement can improve near vision and reduce a person’s dependence on reading glasses. The surgeon performing RLE can utilize a monovision strategy with a distance-correcting lens in one eye and a near-correcting lens in the other, or a multifocal strategy where the lenses provide vision correction across a range of distances.
The best solution for each patient depends on age, current status of distance vision, and personal preference. Consult your eye doctor to determine which of these seven treatments is best for you.


